?What is Diecast (pressure casting)
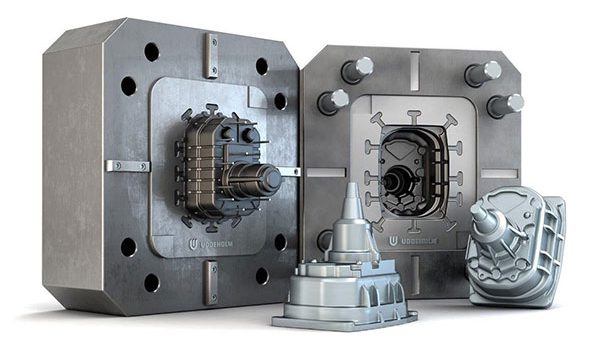
The die-cast mold is a closed enclosure into which molten metal is injected under high pressure and temperature, then it cools quickly so that the solidified part becomes sufficiently rigid and allows it to be removed from the mold. This process uses a cold or hot chamber production technique that relies on high pressure to inject molten metal at speeds of 60 to 100 miles per hour (96 to 160 km) into a reusable steel mold, which is ultimately It leads to the making of a die-cast mold. In this method, parts from a range of durable non-ferrous metals such as zinc, magnesium, aluminum and a set of composite materials are produced.
Disassembly lines and diecast products
One of the most important design parameters for die-cast molds is deciding on the type of parting line that splits the part and creates a contact surface between two or more components. Where the designer places this line depends on the geometric shapes and tolerances of different surfaces. The designer has two choices, either a straight parting line or a broken parting line. You should try to design parts with a straight parting line because it is the least expensive option in terms of tooling cost. When deciding on a parting line, the designer should consider the following factors:
Customer Order – Usually, the customer’s part or product specifications make parting line placement challenging. Mandatory customer requirements also become an issue
Estimating mold costs – A straight parting line can reduce tooling costs. However, in some cases, it will be more economical to design a broken separator line because otherwise the features of the part in question will force you to run a new line, which will cause an overhead cost.
Machining and Finishing – Most parts require post-production machining. Parts of the piece need finishing work and machining. In addition, this part should not need to be beautiful because the effects of the final payments will be visible on the piece.
Molten metal flow – The quality of molten metal injection depends on the proper location of the heart inlet. The mold input should be drawn on the dividing line. This has three advantages. First, it determines whether the casting mold is properly filled with molten metal. Second, under high-pressure casting, the injection or filling mechanism can force the metal into the casting to prevent the part from shrinking during solidification, and third, it can also be paid by finishing the parting line of the mold entrance.
Cores – The position of the cores (the cores create holes in the part) determine where the parting line is located. The designer must consider the location of the core as well as the diameter and length of each core for each hole required in the casting.
During the die-cast mold design process, melt flow is one of the most important considerations. If the mold is not filled accurately, it will lead to defects in the output part. These defects appear in the form of surface lines or air holes in the form of internal mace on the part, which reduces the strength and beauty of the part.
Also, the designer should pay attention to the springs that remove the part from the mold in his design. Blades should be designed to leave minimal marks on the part. One of the advantages of Pran is to prevent the part from bending. The effects of the spring pin on the parts are compressed or embossed in about 0.3 mm. The diameter of the spring pin markings will vary depending on the size of the casting.